
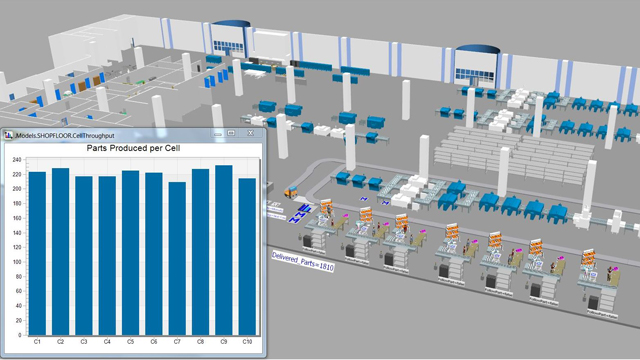
Simulation can be used for physical phenomena, business processes, pedestrian and traffic flow, as well as manufacturing and logistics operations. Train workers in the process and material flow.Analyze the influence of failures and interruptions.Analyze what-if scenarios without interrupting an operating system.Verify resource and buffer utilization, batch sizes, and inventory levels.Optimize control strategies, scheduling, and order sequencing.Analyze system behavior over long time periods and during ramp-upsĭuring the operation phase, simulation can be used to:.Evaluate planning alternatives based on different scenarios.Validate and optimize planning parameters.Determine the required amount of resources, transport systems, buffer sizes.Simulation is particularly useful for analyzing a system, in which its behavior dynamically changes over time and a mathematical solution cannot be calculated at a reasonable effort.ĭuring the planning phase, simulation can be used to: As an integral part of the digital factory concept, simulation helps to shorten time-to-market and supports decision-making processes.
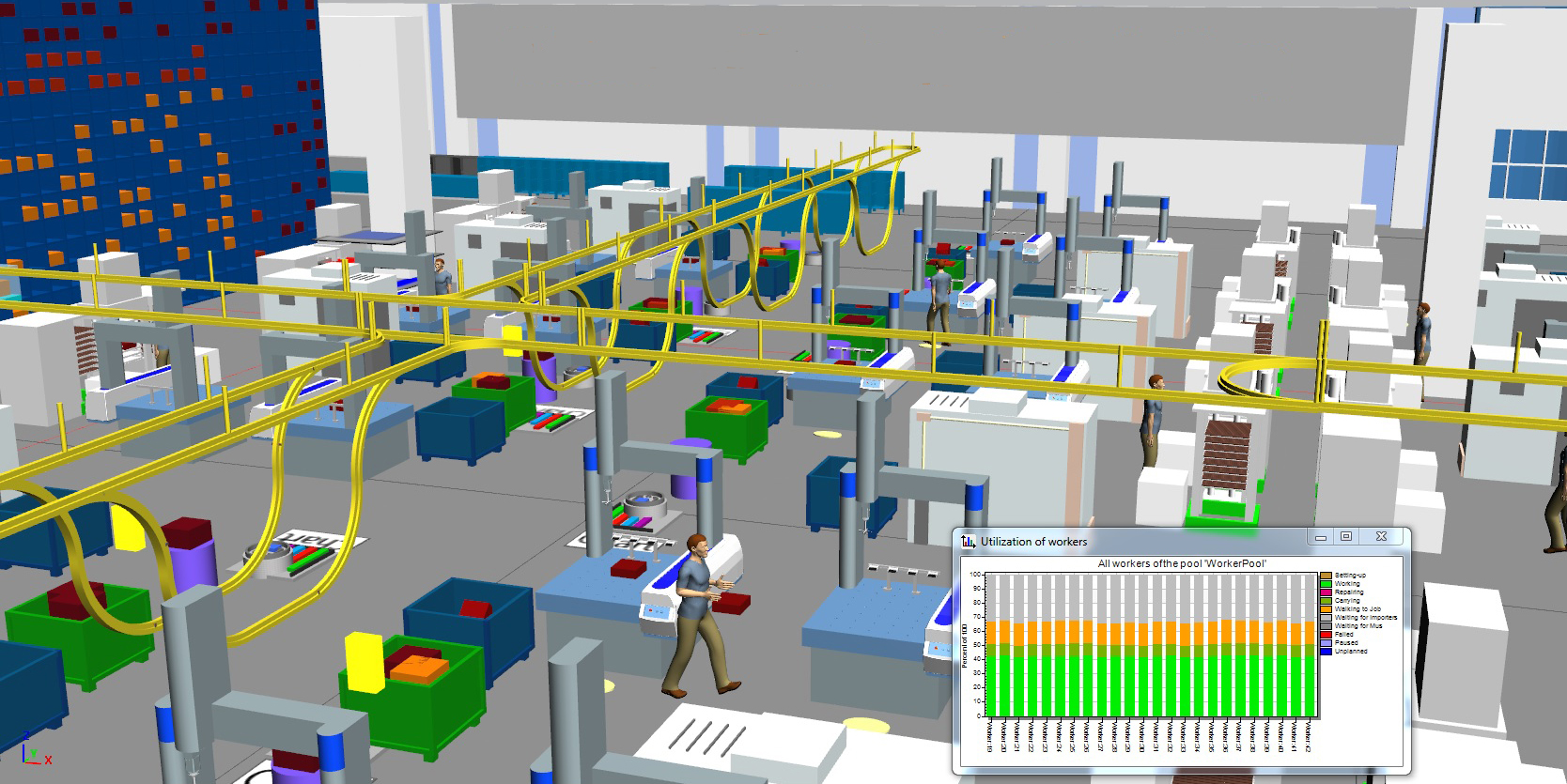

The increasing complexity of products, processes, and systems is one of many reasons why simulation is increasingly used in the planning, implementation, and operation of technical systems. In particular, the processes are developed over time.” (VDI 3633-1, 2010) “Simulation is the representation of a system with its dynamic processes in an experimentable model to reach findings which are transferable to reality. Understand key capabilities and use cases of Plant Simulation.Understand different types of simulation.Understand what simulation is and what benefit simulation provides.After completing this chapter, you will be able to: This chapter will cover theoretical aspects and general understandings of simulation, as well as introduce you to the key capabilities of Plant Simulation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
